Active Area
Active area refers to the region within the sensor's maximum field of view that is used for data acquisition.
By default, the active area covers the sensor's entire field of view. By reducing the active area, the sensor can operate at higher speeds. You can also reduce the active area to exclude areas that are affected by ambient light.
You can choose the active area configuration method, which can be either Point / Size, or Minimum / Maximum.

Active area in an unaligned G5 sensor's scan area, set to smaller than the maximum and shifted upward.
You set the active area in the Inspect > Scan page, in the Active area section under Sensor Properties.
Two active area configuration methods are available in the Configuration Method parameter: Maximum / Minimum and Point / Size (for the parameters related to each method, see the tables below). For instructions on setting active area, see To set a sensor's active area.
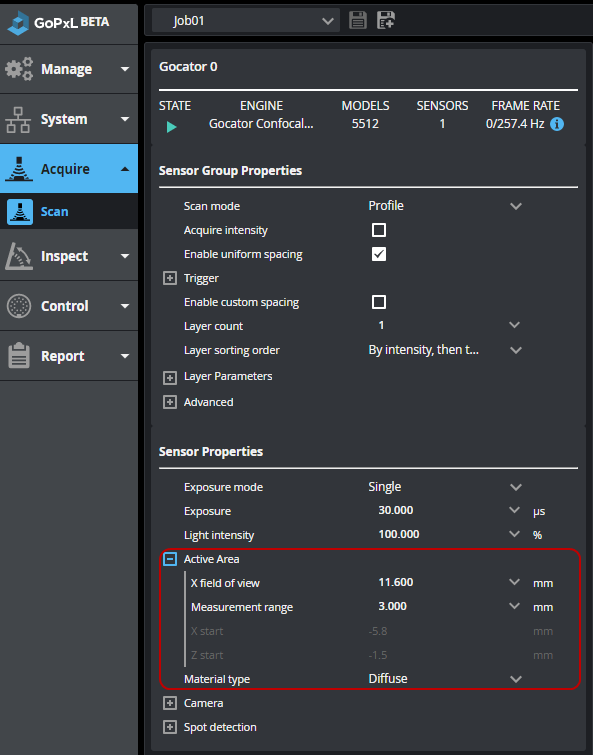
| 1. | Go to Inspect > Scan page. |
| 2. | (Optional) If you are configuring the active area of a sensor in a multi-sensor system, select the correct sensor. |
| 3. | (Optional) Place a sample target in the sensor's scan area, and in the Active Area section, click the Acquire button to get some scan data. |
Getting a scan while setting the active area can help you determine the necessary size and position of the active area.
| 4. | Choose the active area configuration method in Configuration Method. |
One of the following: Point / Size and Minimum / Maximum.
| 5. | Set the active area. |
Adjust the active area graphically in the data viewer using your mouse or enter the values manually in the fields.
Point / Size: For parameter descriptions, see Active area parameters - Point / Size method.
Minimum / Maximum: For parameter descriptions, see Active area parameters - Maximum / Minimum method.
| 6. | Save the changes in the job file. |
To reset the active area
-
Click the Reset button.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Min X Max X |
The minimum and maximum X values. |
|
Min Z Max Z |
The minimum and maximum Z values. |