Modbus TCP Protocol
You can use a Modbus TCP programmable logic controller (PLC) over Ethernet to operate a sensor and receive measurement values. Modbus only supports a subset of the tasks that can be accomplished in the web interface (for example, starting and stopping sensors, and switching jobs). Scan data can't be sent to the PLC.
You configure the protocol on the Control > Industrial page. After configuring the Modbus protocol in GoPxL (see below), use the information in Modbus TCP Protocol Format - PLC Information to configure your PLC.
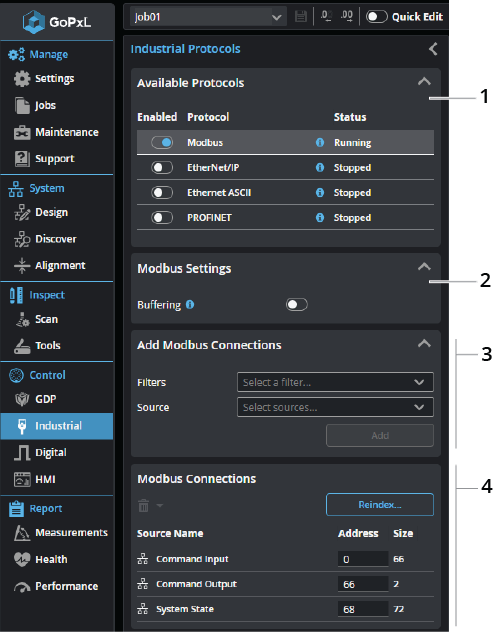
| Element | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Available Protocols |
Click a row in the table to choose which protocol to configure. Enable a protocol by toggling the slider to the right. |
|
2 |
Modbus Settings |
Buffering Toggle the slider to enable/disable buffering of scan outputs. On line profile sensors, buffering should be enabled in Surface mode when Surface Generation Type is set to Continuous mode and if multiple objects may be detected within a time frame shorter than the polling rate of the PLC. If buffering is enabled, the PLC must send the 'Buffer Advance' command to advance the queue before reading the measurement results. For more information, see Control Input. |
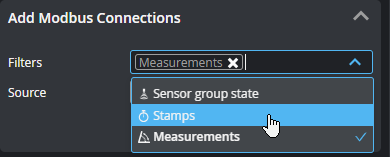
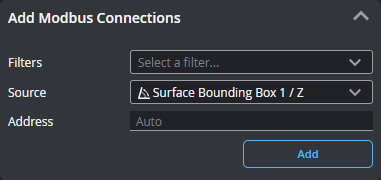
| 3 | Add Modbus Connections |
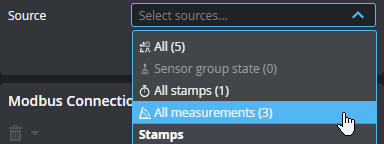
Lets you add sources (such as stamps or measurements) to send over the protocol. Added connections appear in the Modbus Connections section at the bottom of the panel. If you have many sources, you can filter them by type to make it easier to find the source you want in the Source drop-down . You can enable more than one filter.
Choose a source in the Source drop-down. If you leave Address as "Auto", GoPxL automatically increments the value; otherwise, you can set it yourself.
You can also add all sources, or all sources of a given type.
Click Add to add the source to the Modbus Connections table below. |
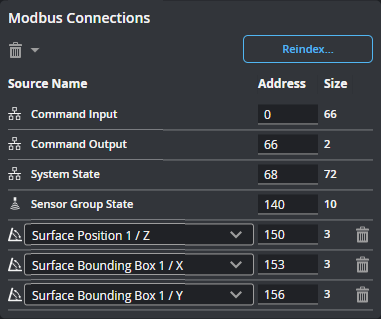
| 4 | Modbus Connections |
The connections listed here will be sent by the protocol to a compatible PLC. You can delete a connection using the trashcan icon in its row, or change its ID. When changing an ID, make sure to use the size of the source to correctly calculate the minimum offset.
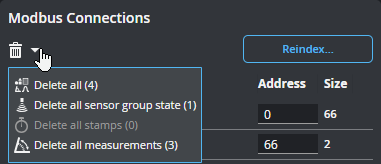
You can also use shortcut commands to delete all of the connections, or specific categories of connections.
Use Reindex... to remove gaps of unused addresses between connections. You can also use Reindex... to set the value of the first index. |