Profile Filter
The Profile Filter tool provides processing filters that you can apply to a uniform profile (not point cloud profiles), letting you process scan data to get more repeatable measurements. You can enable up to seven of the filters at once, in any order. Filters in the tool are chained together. Any Profile tool can use the resulting filtered profile as input.
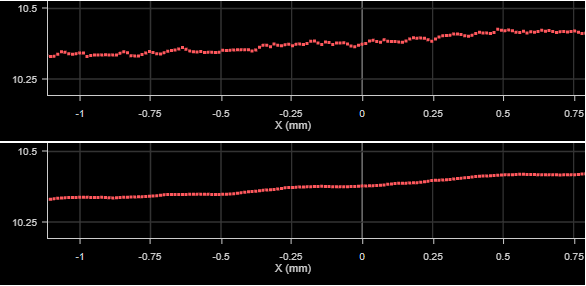
Profile with no filtering (top) and with averaging filter (bottom)
For a list of the filters, see Filters.
The Filter tool provides no measurements or decisions. It only outputs processed profile data.

|
A limited set of filters is also available on the Scan page. These filters let you process scan data without needing to add tools. This can be useful if you are using a sensor mostly as an acquisition device. |
For information on adding, managing, and removing tools, as well as detailed descriptions of settings common to most tools, see Tool Configuration.
Inputs
You configure the tool's inputs in the expandable Inputs section.
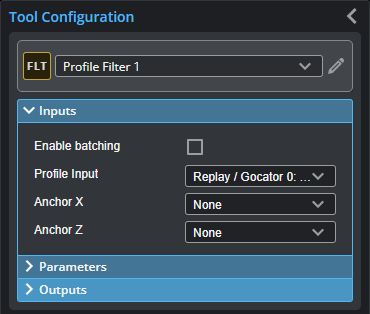

|
To use a measurement as an anchor, it must be enabled and properly configured in the tool providing the anchor. For more information on anchoring, see Measurement Anchoring. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Batching |
For more information on arrays, batching, and aggregating, see Arrays, Batching, and Aggregation. |
|
Profile Input |
The data the tool applies measurements to or processes. |
|
Anchor X or Anchor Z |
The X or Z measurement of another tool that this tool uses as a positional anchor. Positional anchors are optional. |
Parameters
You configure the tool's parameters in the expandable Parameters section.
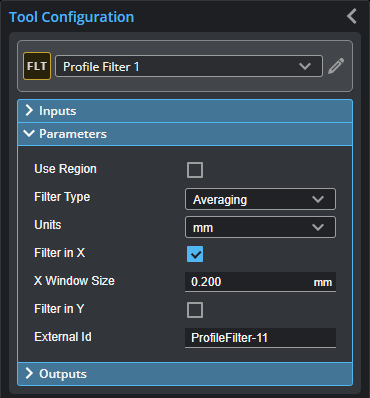
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use Region |
When enabled, displays Region parameters (see below). When disabled, the tool uses all data. |
|
Number of Regions Region {n} |
Lets you set the number of regions, and for each region, the position and dimension. For more information on regions, see Regions. |
|
Filter Type |
The type of filter. For more information on the available filters, see Filters. |
|
Units |
The units the filter uses for the window or windows: points or distance (mm). Not available with all filters. This parameter is only displayed after enabling Filter in X or Filter in Y. |
|
Filter in X Filter in Y |
When enabled, filters along X and Y, respectively, and displays X Window Size or Y Window Size parameters you use to set the window size, using the unit set in Units. (The gap filling and Gaussian filters only let you filter along the X axis.) |
|
Sigma |
The Gaussian curve’s sigma value. (Only displayed with the Gaussian filter and when Filter in X is enabled.) |
The following filters are available in the Profile Filter tool.
Outputs
The tool provides the following output.
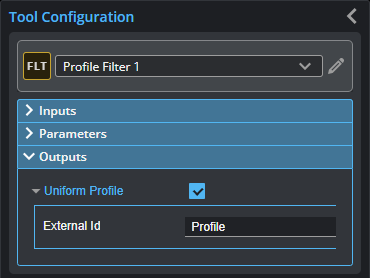
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Profile |
The filtered uniform profile. |